
With nearly 70% of the global population using the internet – and growing by 3% annually – digital accessibility is more critical than ever. In many countries, the days of waiting weeks for letters or traveling long distances to government offices are behind us. Today, many services are just a click away on computers, smartphones, and IoT devices. However, not all government websites provide user-friendly, intuitive designs or easy access to comprehensive information.
Our team at P2H specializes in transforming government platforms into user-friendly interfaces across the Middle East and the United States. In this series of 3 articles, I will delve into the reasons behind the slow progress of digitalization in government, spotlight the positive trends in e-government, and offer strategies for overcoming the sector’s inherent complexities and bureaucratic obstacles.
The Benefits of User-Friendly Government Platforms
A robust online presence is essential for government institutions, offering substantial benefits to both the government and its users, including citizens, organizations, and foreign nationals. These platforms provide faster, easier, and 24/7 access to information and services, eliminating the need for in-person visits to government offices. Additionally, they enable government institutions to monitor processes and outcomes more effectively, while maintaining transparency and accessibility. This fosters long-term relationships and promotes economic development.

Anastasiia Bondarenko, UI/UX Designer at P2H
Governments gain multiple benefits from effective digital platforms, including the ability to:
- Simplify complex bureaucratic processes and enhance transparency.
- Improve user interactions by facilitating feedback and communication.
- Increase efficiency by reducing administrative costs and optimizing resource use.
- Quickly adapt to changes in laws, regulations, or civic needs.
- Reduce corruption through automation and minimize human involvement.
- Accelerate data processing and standardize digital databases.
- Streamline monitoring processes and integrate services into a unified digital ecosystem.
- Ensure high standards of data protection.
- Strengthen the country’s image, promoting economic growth and innovation.
P2H designer Anastasiia Bondarenko adds, “Apart from the obvious functional benefits, the state has less apparent but important reasons to invest in e-government projects. By presenting these platforms in the international market, countries demonstrate their digital maturity. Consequently, they improve their image, attract financial investments, and increase the country’s appeal to tourists and expats.”
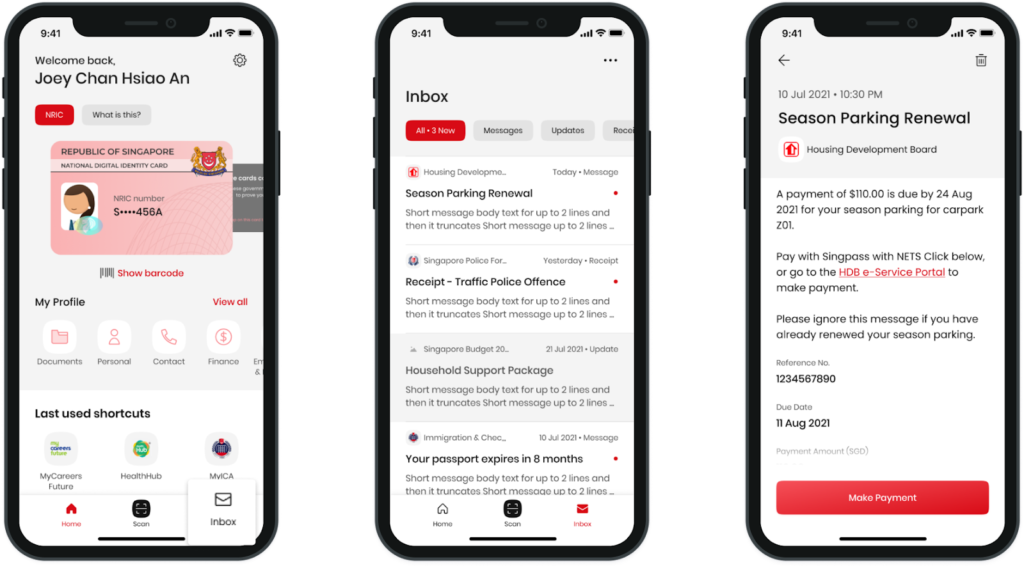
Singpass application. Singapore
Common Challenges with Government Websites
Despite these benefits, many government websites and digital services struggle with usability due to several factors:
1. Outdated Technologies
Many government institutions still rely on technologies, mechanisms, and interfaces developed over a decade ago, making integration with modern solutions difficult. These outdated systems often overlook user experience and lack investment in research, development testing, and implementation of current design strategies.
2. Bureaucracy and Regulatory Constraints
Implementing new technologies or updating existing systems often requires navigating multiple bureaucratic levels, leading to delays. Moreover, regulatory and administrative requirements can further complicate digital transformation efforts, leaving many institutions unprepared for comprehensive reforms.
3. Funding Limitations
Digital transformation is a complex and costly process that requires significant investment. Often, government projects receive limited funding unless they are part of a broader national strategy. As a result, improvements in design are typically minor and constrained by both technological and administrative limitations.
4. Service Complexity
Government services are typically overloaded with information and can become increasingly complex over time. In many cases, minor updates may only offer temporary relief or prove ineffective. This highlights the need for regular, systematic audits of all services and continuous optimization of both online and offline processes to enhance usability and efficiency.
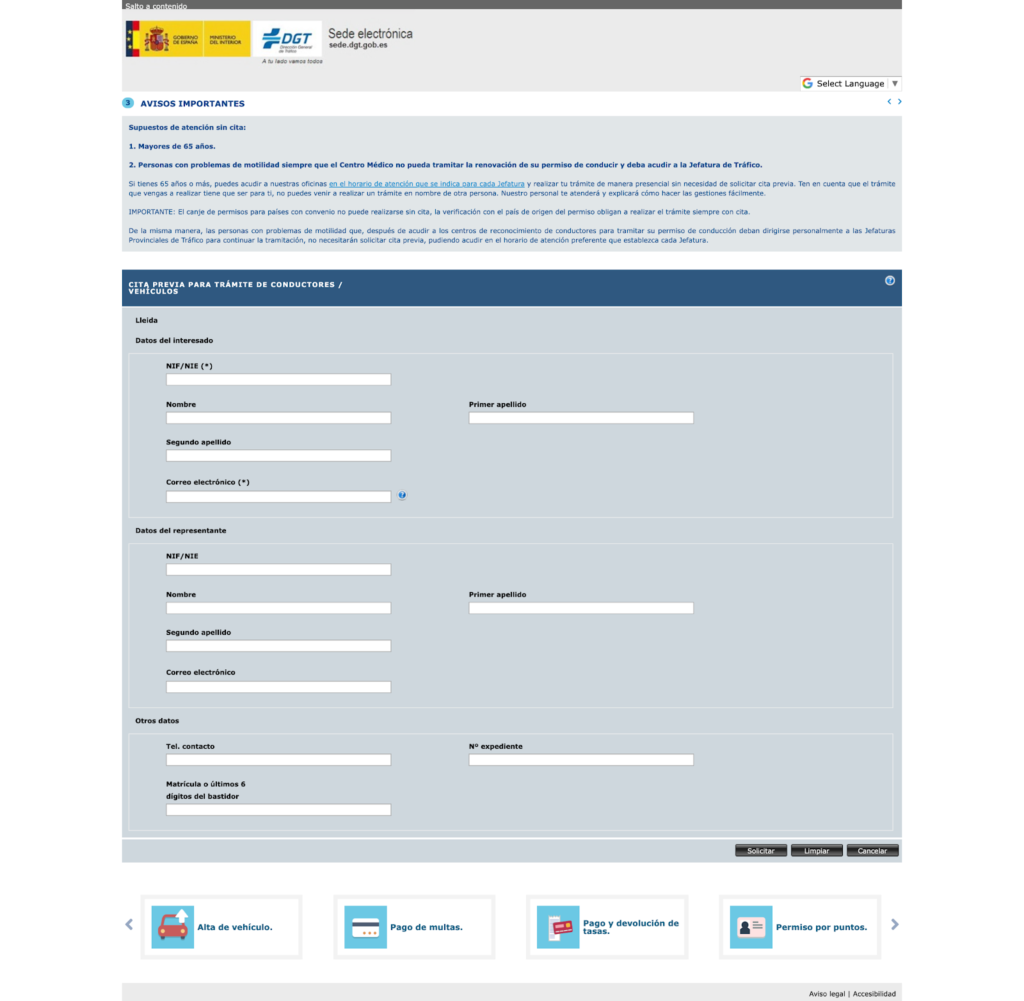
An Example of an Outdated E-Government System Criticized by Many: DGT Spain
But it’s important not to generalize across all government institutions, as many are actively evolving their approach to digital services. In the next article we will go into details of what positive tendencies and changes are to be observed in e-government.
Positive Trends in E-Government
Not all government institutions have out-of-date interfaces and are not user-friendly. Many are actively evolving their approach to digital services. This shift is influenced by factors such as the experiences of other nations, technological advancements, and new legislative initiatives. With the rise in internet and mobile usage and increased digital literacy, (two-thirds of the US population now at least have digital skills) citizens are demanding more modern, transparent, and user-friendly digital products.
Digital platforms are designed not only for citizens but also for government employees, including operators, managers, administrators, and consultants. These e-platforms help internal teams automate processes and simplify daily tasks, leading to greater efficiency.
As demand for better digital services grows, the sector is attracting new talent and expertise, driving a fundamental shift in how governments approach digitalization. Technologies such as AI, Machine Learning, IoT, chatbots, and big data are becoming common, along with security measures like biometric verification and two-factor authentication (2FA), which are now almost standard in EU countries and the US.
Modern Trends and Best Design Practices in the Government Sector
Modern design trends and best practices are increasingly being adopted in the government sector. Design is becoming more standardized with the creation of national and industry-specific design systems, and there is a growing focus on user-centered research and testing. As a result, government services are becoming simpler, more user-friendly, and more adaptable for scaling and integration. The user interfaces (UI) of these platforms are also improving significantly.

Anastasiia Balan, Product / UX / UI Designer at P2H
We are seeing a growing number of government services being optimized for mobile devices, with a strong emphasis on accessibility to ensure inclusivity for people with disabilities. Developing modern, accessible interfaces is a key focus of our work.
As our designer Anastasiia Balan observes, “The well-known ‘Aesthetic Usability Effect’ shows that users perceive aesthetically pleasing designs as more user-friendly and understandable, and they are generally more tolerant of minor issues.”
How to Effectively Work with E-Gov Platforms
A leading example of an effective e-Gov product is Diia in Ukraine.
When designing government platforms, the focus should be on simplicity, functionality, and clarity. While creating aesthetically appealing interfaces can be challenging, it is essential for improving user experience.

Anastasiia Symantieva, UI/UX Designer at P2H
As our designer Anastasiia Symantyeva points out, “Given the varying levels of digital literacy, it’s important to effectively engage with all user groups by maintaining visual design clarity, using straightforward language, and implementing intuitive UI components and patterns.”
The primary task for development teams is to understand the diverse users of government services. This includes identifying their needs, motivations, and expectations, and considering all potential user scenarios, including offline interactions. It’s essential to create solutions that are accessible and effective for a wide range of national, demographic, social, religious, and linguistic groups, including people with disabilities.
To truly understand user pain points and needs, direct communication is key. Conducting research, in-depth interviews, and analyzing data are crucial for formulating accurate user requirements and testing solutions. Ongoing research throughout development ensures the product remains relevant and user-friendly. Even after launch, continuous user engagement through metric analysis and feedback is vital for ongoing improvement.
Some things are rather to be avoided when Designing E-Gov Platforms. What exactly – we talk in the final part of the series.
Things to Avoid When Designing E-Gov Platforms
When developing e-Gov platforms, there are several key pitfalls to avoid:
- Overlooking regional and ethnic user characteristics.
- Skipping essential research and testing phases.
- Disregarding accessibility requirements.
- Failing to understand the administrative, legal, municipal, fiscal, and other relevant processes the product must support.
- Neglecting the integration of the product with other services.
- Not testing localized versions of the platform.
- Using graphic materials that are irrelevant to the specific country or region.

Iryna Movchan, Team Designer at P2H
As our team designer, Iryna Movchan, points out, “When designing interfaces for government clients, it’s crucial to ensure accessibility for people with physical or cognitive impairments, protect users’ information, and develop a mobile-friendly version of the website.”
One unique aspect of government platforms is the lack of alternative or competing products. This creates both an advantage and a significant responsibility: the usability and functionality of these services, as well as how users interact with them, are entirely dependent on the design team’s decisions. Thus, thorough analytics, research, testing, and constant user feedback, and an understanding of regional and national specifics are essential to creating successful e-Gov platforms.
Quick Summary of the series:
User-friendly e-gov platforms allow government institutions to optimize resources, enhance transparency, quickly adapt to legislative changes, and better engage with citizens. Although many governments still struggle with outdated technologies and complex bureaucratic processes, a growing number are embracing modern technologies and prioritizing digitalization. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for accessible and inclusive services that cater to diverse user needs, including those of people with disabilities.


